Breathing is one of the most vital functions for us, yet the impact of the nose on this process is often underestimated. The nose does more than just facilitate the intake and expulsion of air; it plays a critical role in enhancing breathing quality and, by extension, overall health.
The Anatomy of the Nose
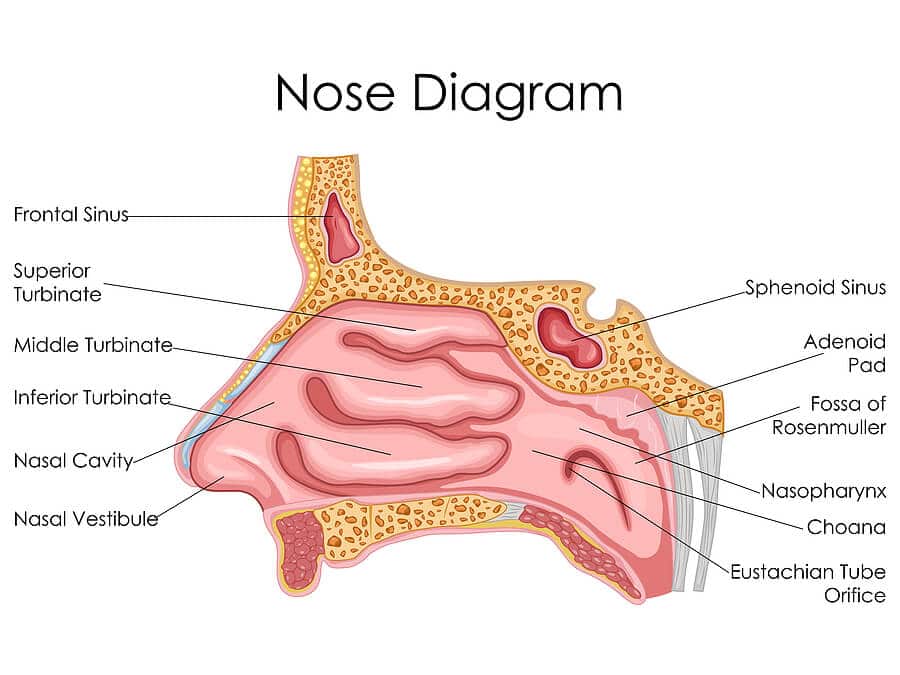
The human nose consists of two nostrils separated by a septum and a detailed internal structure. Inside the nose, three small structures called turbinates serve to filter, warm, and humidify the air. The nasal cavity is lined with mucous membranes and tiny hairs called cilia. These components are essential for ensuring that the air entering the lungs is clean and appropriately conditioned.
Filtering Harmful Particles
One major function of the nose is to filter out dust, pollutants, and pathogens. When air enters the nose, it passes through the nasal hairs that trap larger particles. This helps keep any unwanted substances from reaching the lungs and causing respiratory issues.
Deeper in the nasal cavity, the mucous membranes trap smaller particles and microorganisms. Cilia then sweep this mucus, along with the trapped particles, toward the throat where it can be swallowed and neutralized by stomach acids. This filtration process reduces the risk of infections and lung problems.
Warming and Breathing the Air
Upon inhalation, the air passing through the nose is warmed to one’s body temperature. The turbinates increase the surface area of the nasal passages, greatly aiding in this warming process. Additionally, the air gains moisture as it makes contact with the mucous membranes. Warm, moist air is less likely to irritate the delicate tissues of the lungs and contributes to more efficient gas exchange.
Breathing through the nose allows for better regulation of the amount of air taken in, leading to more efficient oxygen absorption. The longer airway through the nose means air spends more time in contact with the mucous membranes, assisting in the greater release of nitric oxide. This chemical helps expand blood vessels in the lungs, improving oxygen absorption into the bloodstream.
Smell and Its Relation to Taste
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is closely linked to the nose’s structure. Olfactory receptors are located in the upper part of the nasal cavity. Smell significantly impacts the sense of taste since approximately 80% of what is tasted is influenced by smell. Thus, the nose indirectly contributes to the enjoyment and proper digestion of food.
Impact on Sleep Quality
The nose also plays a vital role in regulating our quality of sleep. Proper nasal breathing reduces the likelihood of snoring and mitigates sleep apnea. During sleep, mouth breathing can lead to a dry throat and restless sleep, decreasing one’s overall sleep quality. Optimal nasal airflow ensures a smoother and more restful sleep.
Influence on Respiratory Health
Besides filtering out harmful particles, the nose plays a vital role in the immune system. The mucous membranes contain antibodies and enzymes that serve as the first line of defense against pathogens. The production of mucus increases in response to infectious agents, helping to remove them from the body more efficiently.
Chronic mouth breathing can also lead to respiratory infections. In the long term, it may cause structural changes in the airways, leading to difficulties in breathing and other health complications. Nasal breathing helps maintain one’s respiratory health by ensuring optimal airflow and filtering out any harmful substances.
Practices for Healthy Nasal Function
Keeping the nasal passages clear and healthy is essential. Regularly using saline sprays or performing nasal irrigation can help maintain mucous membrane health. Avoiding excessive exposure to pollutants and allergens also protects the nose’s filtering capabilities. Even staying hydrated ensures that the mucous membranes always remain moist and effective.
Conclusion
The nose is a powerful and essential organ influencing breathing and overall health for all. From filtering the air to enhancing oxygen absorption and affecting sleep quality, its functions are integral to overall well-being.