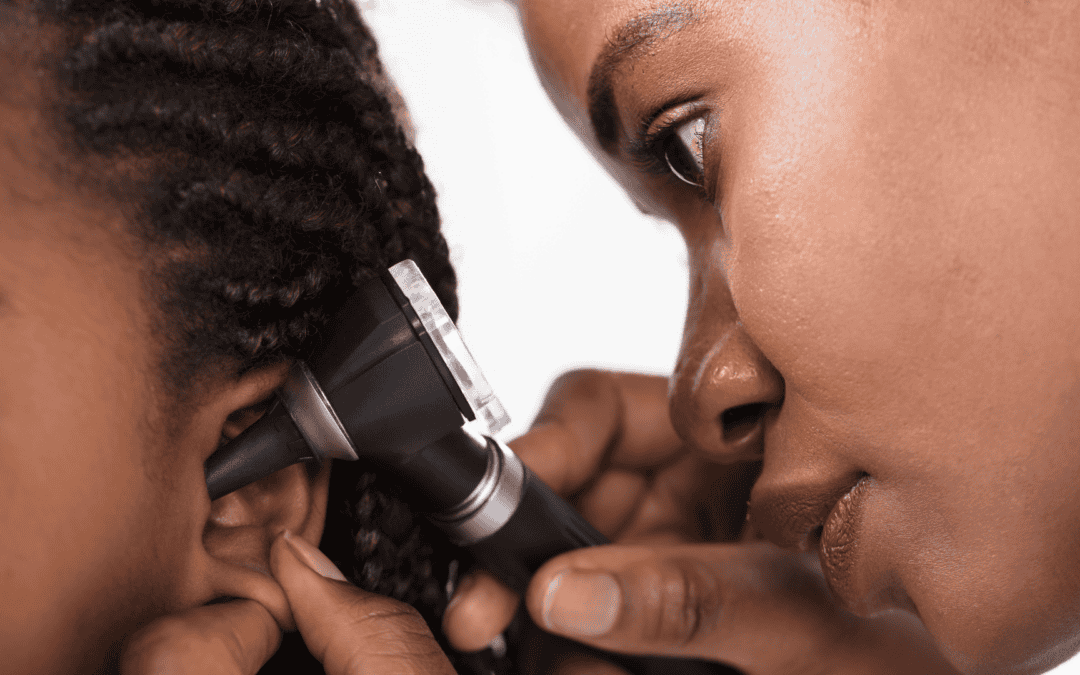
Ear infections are a common issue, especially among children. Understanding these infections can help you recognize symptoms and seek timely treatment.
Types of Ear Infections
There are three main types of ear infections: outer ear infections, middle ear infections, and inner ear infections. Each type affects different parts of the ear and has unique symptoms.
Outer Ear Infections
Outer ear infections affect the ear canal, the tube leading from the outer ear to the eardrum. Swimmer’s ear is the most common type of outer ear infection. This infection occurs when water remains in the ear canal, creating a moist environment ideal for bacteria and fungi to grow.
Symptoms:
- Itching and redness in the ear canal
- Pain, especially when touching the ear
- Fluid drainage from the ear
- Swollen ear canal
Treatment:
- Keep the ear dry and avoid swimming or showering until healed.
- Use over-the-counter ear drops or prescribed antibiotics.
- Pain relief with over-the-counter pain relievers.
Middle Ear Infections
Middle ear infections, also called otitis media, occur behind the eardrum. They often result from respiratory infections that cause fluid buildup. Blocked Eustachian tubes, which connect the middle ear to the back of the throat, can also lead to these infections.
Symptoms:
- Ear pain and pressure
- Trouble hearing
- Fluid drainage from the ear
- Fever and irritability (more common in children)
Treatment:
- Monitor the infection, as many clear up on their own.
- Use pain relievers to ease discomfort.
- In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed.
- For recurrent infections, ear tubes may be recommended.
Inner Ear Infections
Inner ear infections, also known as labyrinthitis, are less common but more severe. These infections affect the inner ear’s structures that aid in balance and hearing. They are usually caused by viral infections, though bacteria can also be responsible.
Symptoms:
- Dizziness or vertigo
- Hearing loss
- Ringing in the ear (tinnitus)
- Nausea and vomiting
Treatment:
- Rest and hydration are vital.
- Use medications to reduce dizziness and nausea.
- Antibiotics are necessary if a bacterial infection is suspected.
- Physical therapy might be suggested for balance issues.
Causes of Ear Infections
Ear infections are often caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Several factors can increase the risk of developing an ear infection.
- Upper Respiratory Infections: Colds and the flu can lead to infections in the ear.
- Allergies: Inflammation from allergies can block the Eustachian tubes.
- Ear Wax Buildup: Excessive ear wax can trap bacteria in the ear canal.
- Swimming: Water in the ear can promote bacterial growth.
- Injuries: Scratches or other injuries to the ear canal can lead to infections.
- Temperature and Humidity: Warm, humid conditions can foster bacteria and fungi.
Recognizing Symptoms
Pay attention to the symptoms of ear infections to seek timely treatment. Common symptoms across all types of ear infections include ear pain, fluid discharge, and hearing changes. Additionally, fever and irritability may indicate an infection in children.
Preventing Ear Infections
While not all ear infections are preventable, several measures can reduce the risk.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Regular handwashing can prevent the spread of infections.
- Avoid Inserting Objects: Keep cotton swabs and other objects out of the ear.
- Dry Ears After Swimming: Use a towel to dry the ears thoroughly.
- Use Earplugs: Prevent water from entering the ears while swimming.
When to See a Professional
If you or your child experience severe symptoms, such as intense pain, persistent fever, or sudden hearing loss, it is important to consult a professional immediately. Additionally, seek medical advice if symptoms do not improve within a few days or worsen.
Treatment Options
Treatments for ear infections vary depending on the type and severity of the infection. A professional may recommend a combination of at-home care and medical treatments. Over-the-counter pain relievers, antibiotics, and ear drops are common treatments. In severe cases, surgical intervention, such as ear tubes, may be necessary.
Conclusion
Ear infections are common, but understanding their types, symptoms, and treatments can help manage them effectively. By recognizing the signs and knowing when to seek medical help, you can ensure prompt treatment and reduce the risk of complications. Remember to practice good ear hygiene and take preventative measures to protect your ears from infections.